Logarithmic Equations*
Learning Objectives
- Solve a logarithmic equation with algebra
- Solve a logarithmic equation with a graph
- Use the one-to-one property of logarithms to solve a logarithmic equation
- Solve a radioactive decay problem
We have already seen that every logarithmic equation logb(x)=y is equivalent to the exponential equation by=x. We can use this fact, along with the rules of logarithms, to solve logarithmic equations where the argument is an algebraic expression.
For example, consider the equation log2(2)+log2(3x−5)=3. To solve this equation, we can use rules of logarithms to rewrite the left side in compact form and then apply the definition of logs to solve for x:
log2(2)+log2(3x−5)=3 log2(2(3x−5))=3 log2(6x−10)=3 23=6x−10 8=6x−10 18=6x x=3Apply the product rule of logarithms.Distribute.Apply the definition of a logarithm.Calculate 23.Add 10 to both sides.Divide by 6.
A General Note: Using the Definition of a Logarithm to Solve Logarithmic Equations
For any algebraic expression
S and real numbers
b and
c, where
b>0, b=1,
logb(S)=cif and only ifbc=S
Example: Using Algebra to Solve a Logarithmic Equation
Solve
2lnx+3=7.
Answer:
2lnx+3=7 2lnx=4 lnx=2 x=e2Subtract 3.Divide by 2.Rewrite in exponential form.
Try It
Solve
6+lnx=10.
Answer: x=e4
Example: Using a Graph to Understand the Solution to a Logarithmic Equation
Solve
lnx=3.
Answer:
lnx=3x=e3Use the definition of the natural logarithm.
Below is a graph of the equation. On the graph, the x-coordinate of the point at which the two graphs intersect is close to 20. In other words e3≈20. A calculator gives a better approximation: e3≈20.0855.
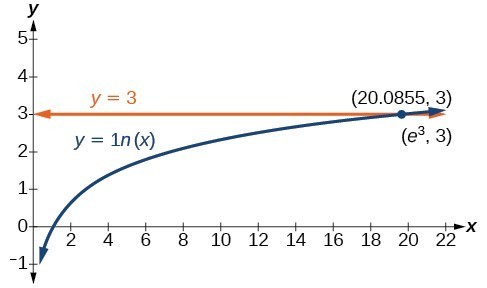
The graphs of
y=lnx and y = 3 cross at the point
(e3,3), which is approximately (20.0855, 3).
Try It
Use a graphing calculator to estimate the approximate solution to the logarithmic equation
2x=1000 to 2 decimal places.
Answer: x≈9.97
Use the one-to-one property of logarithms to solve logarithmic equations
As with exponential equations, we can use the one-to-one property to solve logarithmic equations. The one-to-one property of logarithmic functions tells us that, for any real numbers x > 0, S > 0, T > 0 and any positive real number b, where b=1,
logbS=logbT if and only if S=T.
For example,
If log2(x−1)=log2(8),then x−1=8.
So, if x−1=8, then we can solve for x, and we get x = 9. To check, we can substitute x = 9 into the original equation: log2(9−1)=log2(8)=3. In other words, when a logarithmic equation has the same base on each side, the arguments must be equal. This also applies when the arguments are algebraic expressions. Therefore, when given an equation with logs of the same base on each side, we can use rules of logarithms to rewrite each side as a single logarithm. Then we use the fact that logarithmic functions are one-to-one to set the arguments equal to one another and solve for the unknown.
For example, consider the equation log(3x−2)−log(2)=log(x+4). To solve this equation, we can use the rules of logarithms to rewrite the left side as a single logarithm, and then apply the one-to-one property to solve for x:
log(3x−2)−log(2)=log(x+4) log(23x−2)=log(x+4) 23x−2=x+4 3x−2=2x+8 x=10Apply the quotient rule of logarithms.Apply the one to one property of a logarithm.Multiply both sides of the equation by 2.Subtract 2x and add 2.
To check the result, substitute x = 10 into log(3x−2)−log(2)=log(x+4).
log(3(10)−2)−log(2)=log((10)+4) log(28)−log(2)=log(14) log(228)=log(14)The solution checks.
A General Note: Using the One-to-One Property of Logarithms to Solve Logarithmic Equations
For any algebraic expressions
S and
T and any positive real number
b, where
b=1,
logbS=logbT if and only if S=T
Note, when solving an equation involving logarithms, always check to see if the answer is correct or if it is an extraneous solution.
How To: Given an equation containing logarithms, solve it using the one-to-one property.
- Use the rules of logarithms to combine like terms, if necessary, so that the resulting equation has the form logbS=logbT.
- Use the one-to-one property to set the arguments equal.
- Solve the resulting equation, S = T, for the unknown.
Example: Solving an Equation Using the One-to-One Property of Logarithms
Solve
ln(x2)=ln(2x+3).
Answer:
ln(x2)=ln(2x+3) x2=2x+3 x2−2x−3=0(x−3)(x+1)=0 x−3=0 or x+1=0 x=3 or x=−1Use the one-to-one property of the logarithm.Get zero on one side before factoring.Factor using FOIL.If a product is zero, one of the factors must be zero.Solve for x.
Analysis of the Solution
There are two solutions:
x = 3 or
x = –1. The solution
x = –1 is negative, but it checks when substituted into the original equation because the argument of the logarithm functions is still positive.
Try It
Solve
ln(x2)=ln1.
Answer: x=1 or x=–1
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175..
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2.
- Question ID 2637, 2620, 2638. Authored by: Greg Langkamp. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 98554, 98555, 98596. Authored by: Michael Jenck. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 14406. Authored by: James Sousa. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 122911. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
 The graphs of and y = 3 cross at the point , which is approximately (20.0855, 3).
The graphs of and y = 3 cross at the point , which is approximately (20.0855, 3).